Manufactured Wood (Types, Uses & Comparison)
This guide to manufactured wood shares what it is, types for furniture & flooring, durability, and how these materials compare to solid, engineered-wood, particleboard, and MDF.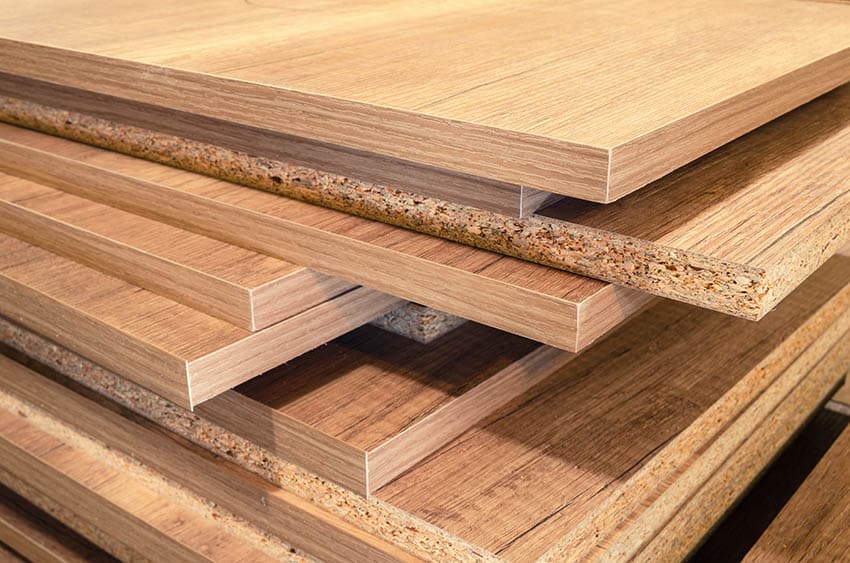
Nowadays, manufactured wood is most often used since it is debatably the type that Is most easily accessible. Additionally, it has a larger spectrum of uses, is more adaptable, and is less expensive than solid wood.
Truly, manufactured wood can resist a greater temperature range, adjust to fluctuations in temperature, endure significantly heavier pressures, and is more straightforward to install than individual elements of wood.

Upload a photo and get instant before-and-after room designs.
No design experience needed — join 2.39 million+ happy users.
👉 Try the AI design tool now
As a result, it is an excellent option to be used as a flooring, furniture, or structural material.
What Is Manufactured Wood?

Manufactured, also known as engineered wood, has been transformed and upgraded by mixing and compressing different wooden pieces with other substances, such as adhesives and sawdust. The upper surface of manufactured wood is a genuine material often treated with melamine.
Underneath the upper surface of the engineered sheet is a pressed board. This material is mainly made of wood, although it is a composite type. It has a comparable look and feel to plywood, a commonly used construction material throughout most houses.
Manufactured woods are stacked in thin sheets on top of one another and crushed to be homogeneous, producing a single uniform piece.
Depending on your selected components, these layers might lend distinct qualities to your work with the manufactured product. Resistance, heat retention, versatility, and lifespan are all desirable qualities of these manufactured materials.
The advantage of using manufactured materials over types of hardwood, oak, or pine is that you do not need to settle on any specific attribute you want it to acquire.
Is Manufactured Board Durable?

Yes! Manufactured wood has exceptional properties and is extremely durable. Due to the various layers of wooden panels and the placement in a crosswire orientation, the strength of the produced material is also quite strong, making it suitable even in high-traffic areas such as floors. Natural veneers or top-quality laminates improve the appearance and sturdiness of their surfaces.
High-quality manufactured surfaces are exceptionally durable and moisture-resistant. It is even ideal to be applied in kitchens and bathrooms. It is also perfect for building modular kitchens, staircases, bookcases, and closets.
Because these manufactured products are stronger than solid lumber, it is more resistant to dents and scratches, which would be important since floors are more prone to these occurrences.
Nonetheless, you must use high-quality manufactured wood for this. If not, there might be a problem, especially with flooring, that will cause the entire surface to rot. Thus, when it comes to a crucial usage like flooring, you must constantly acquire top-grade manufactured products.
What Is This Wood Material Made Of?

Manufactured wood, also marketed as MDF, is frequently made of gluing sawdust, fibers, and tiny bits of genuine material together with high-quality adhesives. It can also be referred to as engineered, mass timber, or artificial wood.
Moreover, manufactured materials come in a variety of patterns, colors, textures, and sizes and is commonly applied in indoor settings, while it can also be found in some outdoor spaces. Oiled, lacquered, untreated, and brushed are the most prevalent manufactured wooden finishes.
Manufactured products are created by combining and binding practically any type of wood, whether softwood or hardwood. Nonetheless, some producers choose to make manufactured items from distinct varieties in order to achieve certain purposes.
Types of Engineered Wood
Various types of manufactured wood are currently available. The most common types of manufactured products, as well as their descriptions, are mentioned below.
Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF)
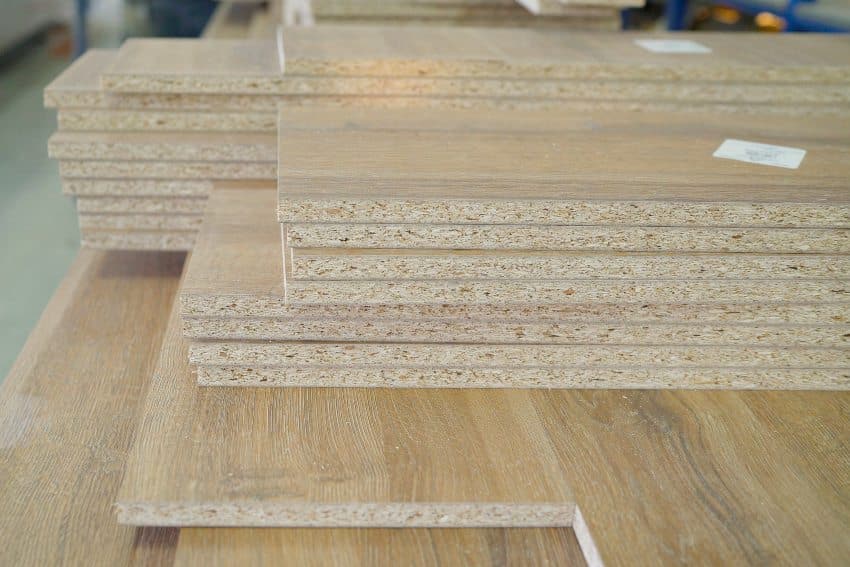

Because of their excellent properties, medium-density fiberboards are the most widely used manufactured wood. MDF has a considerable density and strength, and they are substantially more inexpensive than solid woods. Adhesives and sawdust are used to make medium-density fiberboards.
They will initially dehydrate and remain in high temperatures. They will then fuse together using resins to produce the result. Eventually, they will cut to precise measurements with massive machinery.
Additionally, medium-density fiberboards are widely regarded as the ultimate alternative to genuine wood. They use repurposed materials, which is beneficial for the environment.
Countless designers and contractors have handled MDF for numerous years, and the vast majority of them have performed effectively in production and maintenance. You can enjoy them for years if you maintain them properly.
Furthermore, medium-density fiberboard is a multifunctional construction material. It is indeed inexpensive and suitable for cabinetry, shelves, storage units, and other ornamental applications. See pictures of MDF kitchen cabinets here.
It has a smooth texture that is ideal for painting. MDF’s color ranges from beige to dark brown. Dealing with MDF is comparable to dealing with other popular types, such as plywood.
MDF, unlike actual wood, does not expand and shrink when subjected to heat and moisture. It is simpler to mold and paint in a range of colors than solid hardwood.
Interestingly, there are no knots in the surface of MDF, which can make it difficult to attach a piece. Furthermore, due to the chemicals involved in its production, MDF is impervious to pests like termites.
Plywood
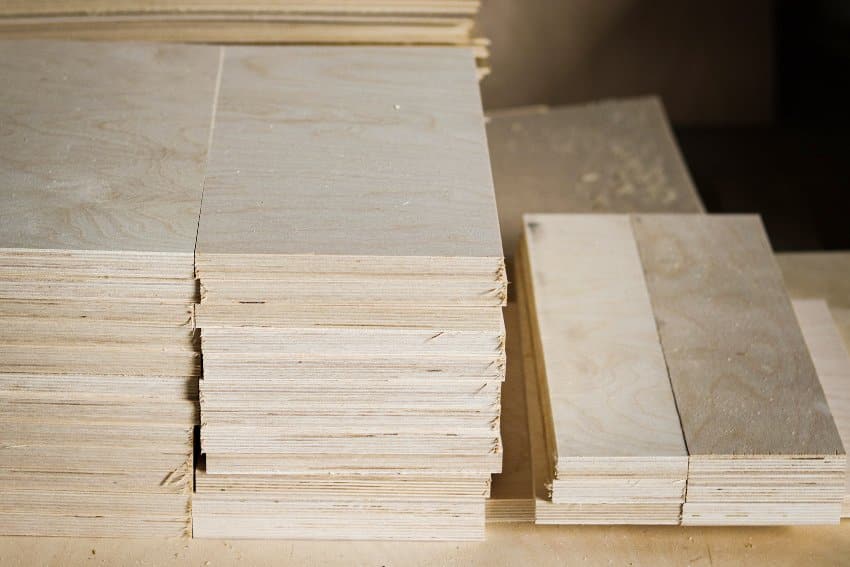

Plywood is believed to be the most durable manufactured wood since it is made by piling many layers of veneers until a durable and seamless solid board is formed.
Shrinking and expanding qualities will regulate as a result of attaching veneers crosswire across the grain. The volume of veneers in plywood affects its quality and quality.
Aside from that, plywood is a hybrid material made out of resin and wood fiber layers that are supplied in panels. Face veneers on a standard plywood panel are usually of greater quality than core veneers.
The core levels’ role is to enhance the spacing between the outermost parts, wherein the bending pressures are largest, hence increasing resistance to bending stresses.
Plywood materials are frequently utilized for both structural and non-structural applications in either wet or dry operating situations – subflooring, single-layer flooring, wall building, roofing, floor sheathing, solid insulated panels, as well as concrete formwork are all included.
High-quality plywood can withstand lateral pressures such as strong wind and earthquake pressures and is an essential component of the structural membrane.
Furthermore, plywood can be used as foundation sheathing as well as finishing cladding. Specialized plywood is obtainable in a variety of designs and textures for exterior cladding uses, merging the natural features of wooden surfaces with robustness and firmness.
High Density Fiberboard (HDF)
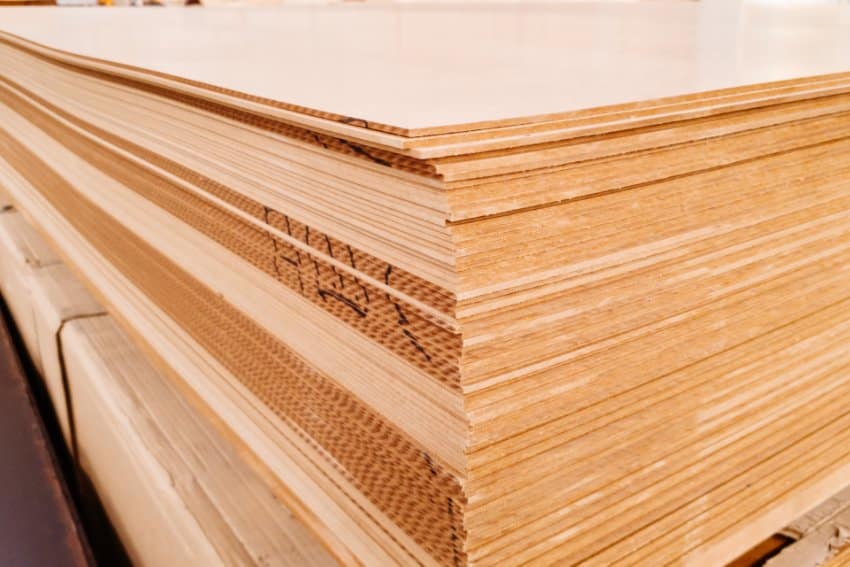

If you think MDF is not ideal for your project in terms of durability, high-density fiberboard, HDF, would be a great alternative. HDF is made in the same manner that MDF is.
Wood fibers made from discarded pieces and fibers are hot-pressed and then joined firmly under extreme pressure with artificial resin binders. Nevertheless, it differs from MDF in numerous important aspects. For starters, HDF is quite dense.
This places HDF in the very same classification as genuine greenheart and ebony-wood. It is considerably more structurally stable than MDF, which means it does not lose shape due to temperature fluctuations.
Even though it is less popular than MDF since the majority of consumers prefer MDF, HDF is one of the greatest substrates for laminated flooring since it is exceptionally durable and strong. You can also find HDF kitchen cabinets that are rising in popularity.
If you seal all the sides thoroughly, it is additionally quite water-resistant. Aside from floors, HDF is frequently used to construct wardrobes, cabinets, wall panels, and display shelving.
Particleboard
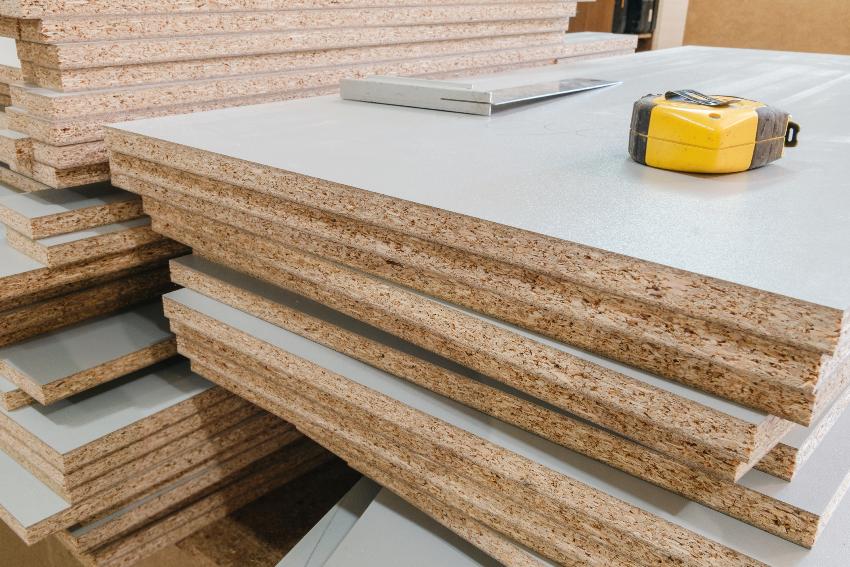

Particleboard is a low-cost flat board created by gluing adhesives to sawdust as well as resins. It is often used in low-cost wood production. Woodworkers primarily use veneer to strengthen it, beautify its appearance, and make it more stain-proof.
Particleboards are commonly used in low-class furniture, underlayment, floors, ceilings, door frames, and wall panels. It is a versatile, low-cost option with numerous advantages.
Moreover, particleboard is an excellent core component for doors since it offers a seamless and level surface that quickly adheres to the door body and has a high screw-retaining ability for installing hinges. Particleboard is also used to create artificial ceilings.
This is due to the particleboard’s excellent thermal insulation. They are also utilized as ceiling panels in a variety of structures.
Particleboards are also used to make dressing tables, tabletops, kitchen cabinets, shelves, bookcases, shoe racks, and bed frames.
They are also commonly used to make speakers since they absorb sound quite well. Hence, they are also seen on the floors and walls of music studios, concert halls, and media spaces for this purpose.
Fiberboard
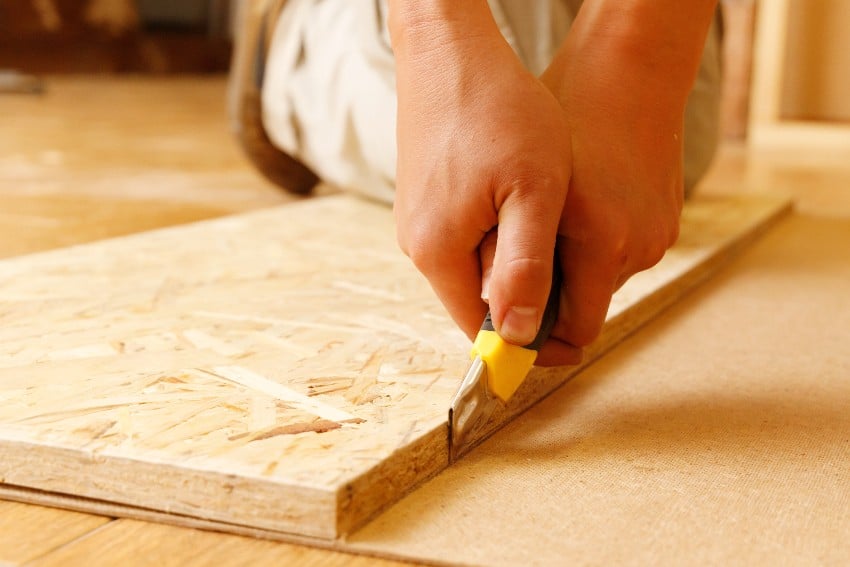

Fiberboard is a thicker board when compared to other kinds of manufactured wood. It is far less prone to cracking and chipping.
Fiberboards are made by cutting boards into smaller parts and heating them until they become fibers. The fibers then dry and join collectively with adhesives to generate fiberboards.
In addition, fiberboard is normally made up of 90% wood and has a uniform texture, consistent strengths in all directions, and a high bending capacity.
Furthermore, fiberboard is not prone to warping and fracturing, and it completely eliminates its flaws. Hard-quality fiberboard can be utilized as a wall slab, door panel, flooring, furniture, and other decorative elements.
Wood Veneer
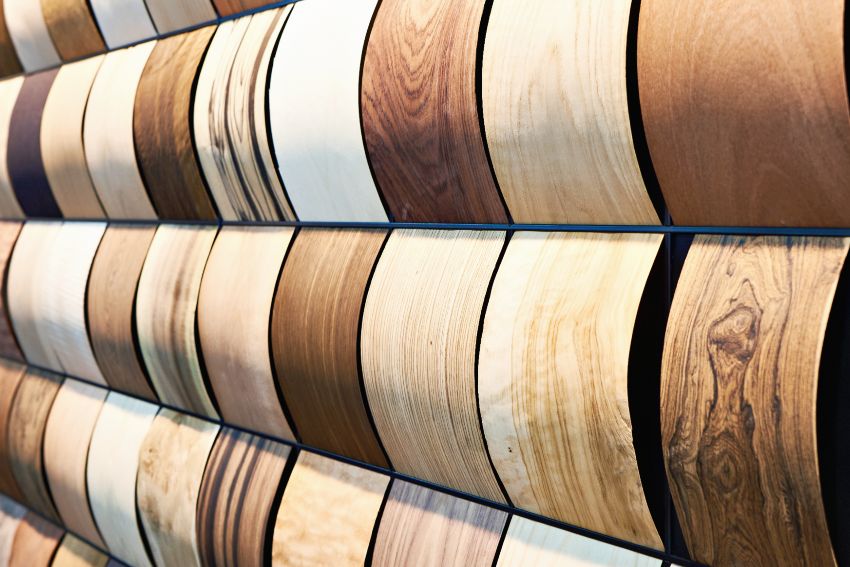

The veneer, which is compressed onto core panels, is a thin piece or sheet. It is made of natural wood that has been scraped and bonded with particleboard, MDF, or plywood. There are numerous veneer grades with numerous applications.
It is also utilized as an element in various sorts of producing wooden products. In actuality, wood veneers are a classic and functionally crucial part of furniture-making that is still used in current architecture.
Normally, a veneer is a “paper-thin” piece of wood used in carpentry. It is typically used to encapsulate and support a solid core surface such as furniture-quality MDF or surface structure. When creating built-in furniture or something with a mechanism, the role of wood veneer is vital.
Cross Laminated Timber (CLT)

Furthermore, CLT panels are often utilized as partitions, floors, walls, and other pieces of furniture. Thicker versions of cross-laminated timber panels can also be used to construct ceilings, platforms, columns, and roofs.
Oriented Strand Board (OSB)
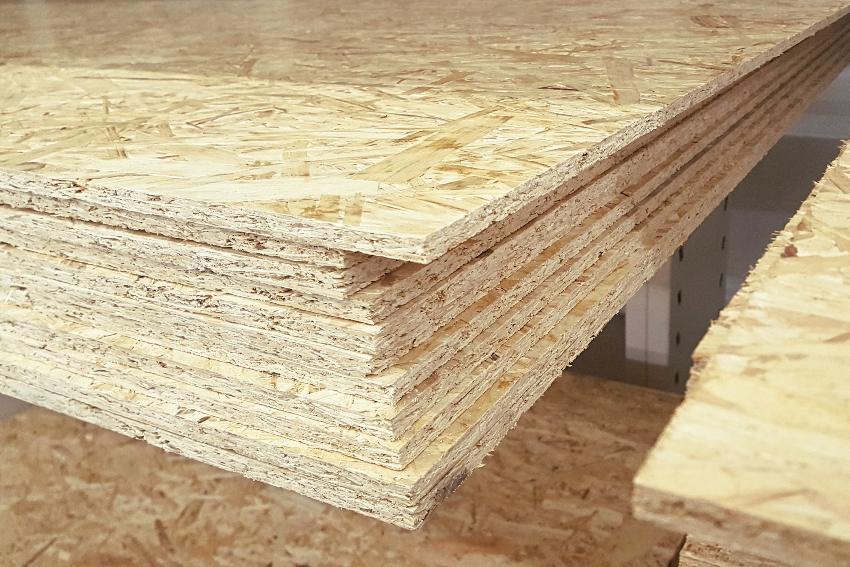

Oriented strand board (OSB) is another form of manufactured wood that is becoming extremely prevalent nowadays. This is constructed of watertight and heat-cured adhesive as well as cross-oriented sheets of rectangular-shaped wood fibers.
This provides it with the same strength as plywood in terms of resistance to bending, warping, and twisting. It is, nevertheless, waterproof, unlike plywood.
The most typical applications for OSB are roof installation, wall cladding, and floor insulation. It can, nonetheless, be used as the web component for prefabricated I-joists as well as the surface layer for structurally insulated boards.
Can It Be Used for Furniture?

Manufactured wood is a superior option for furniture to any other variety due to its aesthetic appearance, machinability, screwing and nailing ability, workability, smoothness of the top, and simplicity of painting.
Flooring

Although solid timber wood is the most popular option for wooden floors, manufactured types also perform admirably and cost less. Due to the high cost of solid wood, manufactured products have become the preferred flooring material with certain enhancements.
The advantages of manufactured materials are numerous, and it is quite durable. The hardness of produced surface treatments used in flooring is also quite strong due to the several layers of wood panels and their placement in a crosswire pattern.
Most significantly, manufactured paneling is simple to maintain when painted and stained. It is simpler to care for and lasts a long time.
Since manufactured types are firmer than genuine, it is more resistant to scratches and fractures, which is important since floors are usually high-traffic.
Since it is easy to paint and stain, inexpensive, ecologically friendly manufactured lumber would be an excellent flooring solution. Although manufactured materials are terrific for flooring, only high-quality products should be used.
What Makes It Different from Solid Wood

It is easy to confuse manufactured wood with solid timber unless you have a keen eye. This is because manufactured products are often layered with natural – creating a veneer. However, the differences between it and solid lumber are as stark as day and night.
For starters, solid hardwood is obtained from trees. That means they are as genuine as they can be. They are created from a solid piece of timber and do not include any adhesives or glue.
All of the sections, from the exterior bark to the core, are cellularly connected. This naturally increases their durability.
The opposite is true with manufactured lumber, which is essentially a compressed mixture of organic materials coupled with non-natural chemicals. The veneer that envelopes the composite panel is the sole thing made of all-natural material.
In addition, if you stare at a slab of manufactured sheet from the sides, you can see the levels that build it up. However, the same does not apply to solid wood slabs.
Is There Any Difference Between Manufactured and Engineered Wood?
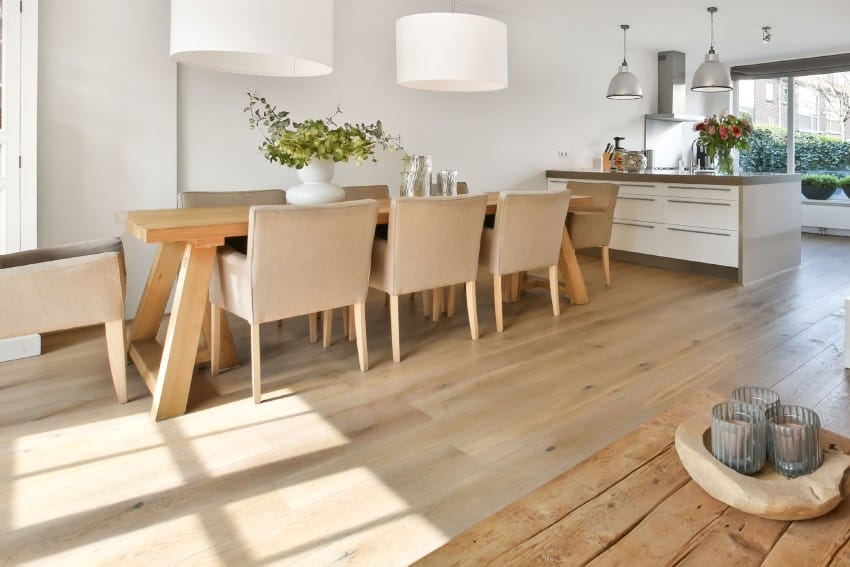

Manufactured and engineered products are generally the same. Engineered is merely the other term for manufactured since it is a wood derivative material formed by binding or fastening fibers, particles, or strands altogether using adhesives or other means of the engineering process to make composite products.
For more related ideas, take a look at our gallery of Engineered hardwood flooring in the kitchen to put together a cohesive design you’ll love.
What Is Particle Board?

There is no difference between manufactured wood and particle board. Particle board, as previously indicated, falls under the category of manufactured products. Particle board is made by compressing and forming various wooden byproducts such as shavings, sawmill wastes, and sawdust.
What Is MDF?
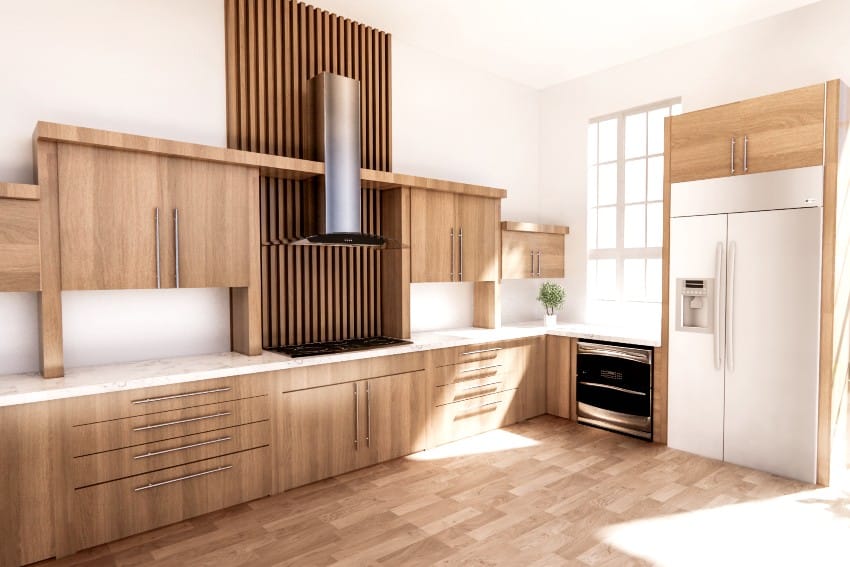

Manufactured wood is a broad word for any derivative timber product created by gluing together fragments, sawdust, and scrap. It is a generic category that includes variants including medium-density fiberboard (MDF).
Because they are tougher, more durable, and eco-friendly, both of these wooden variants have replaced genuine lumber in indoor and outdoor construction projects. They are also simple to handle, accept paint and adhesive well, and feature a seamless finish.
Manufactured wood is a vast range of construction materials that are created artificially by integrating various layers of lumber that have been treated with chemicals under high temperatures and pressure. Each material includes a distinct production method, and the end result has enhanced structural support.
Medium-density fiberboard, on the other hand, is an excellent choice for numerous domestic and commercial construction projects. It may also fall under the category of manufactured wood.
It is made by reusing hardwood and softwood scraps. Such byproducts are ground, dried, and then combined with resins and waxes in a defibrillator at high temperatures and pressure to create massive wood boards.
See more related content in our article about wood flooring patterns on this page.