Sanded Vs Unsanded Grout (Design Guide)
When installing tiles – be it for flooring, walls, backsplash, counters, or others – aside from choosing the proper size, shape, and type of tile materials, you must consider the grout. Choosing between sanded and unsanded grout can really make a difference when it comes to looks, cost, and durability.
Grout is the mortar used to bind tiles together. It is basically a mixture of cement and water; however, there is also a type of grout known as epoxy-grout which has resin and hardener added.
Types of Grout Mixtures
Traditionally, cement-based grouts are used in residential applications, such as when installing tiles for a bathroom wall or kitchen backsplash.
Epoxy grouts are a bit hardier and can stand up to harsh conditions, so they are usually used for outdoor tile installations. They are also resistant to corrosive materials like grease or acid, so they may be used in garages.
Difference Between Sanded and Unsanded Grout
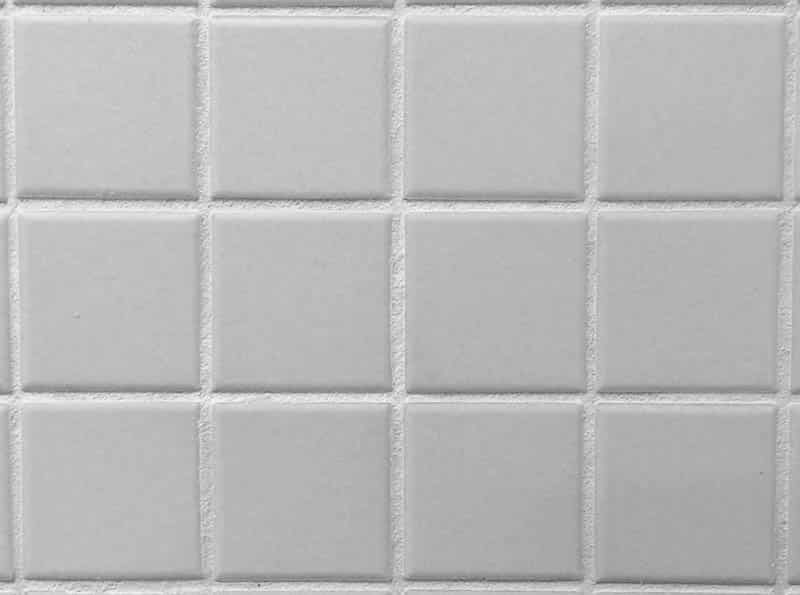
Both cement-based and epoxy-based grouts are commercially available in two types: sanded and non-sanded. The main difference between the two is if there is sand in the mixture or not.
Depending on the types of tile you are installing and the space you are leaving between them, one type can be more advantageous than the other. Let’s look at both types to see how sanded vs. unsanded grout stacks up for your next project.
What is Sanded Grout?
Whether it be cement-based or epoxy-based, sanded grout has a third main ingredient – sand. The addition of sand to the mixture makes it thicker and prevents it from shrinking around the joints between the tiles. Because of its bulk, sanded is best for working with wide joints. It is also a more budget-friendly choice since sand is inexpensive.
When Should I Use Sanded Grout?
If you are installing tiles with joints wider than 1/8 inch you should use sanded grout.
While it is possible to use sanded grout on joints that are less than 1/8 inches, the bulkiness of sanded materials might make it difficult to get the proper amount in joints this small. You might end up with uneven grout lines.
If you are working with joints that are larger than 3/8 inches, you will need to get sanded grout that has a large proportion of sand. This will be labeled as “wide-joint” grout and can be easily found in hardware stores.
Sanded grout is often used in flooring applications since it can hold up better to the pressure of foot traffic. One may use sanded type for a bathroom floor tile and unsanded for a shower wall.
Finally, sanded products have more color options for those looking for a wider variety of options.
What Is Unsanded Style Grout?
Unsanded grout, be it cement or epoxy-based, does not have sand added. Because of this, it has a smoother texture once it has dried. It is also lighter, which can be advantageous but can also make it prone to cracking.
Since unsanded tiles are often used with sensitive tile surfaces, they may require more skill/experience to install them, especially when used with fragile or different tile shapes. However, using unsanded is often easier to work within a vertical application than using a sanded mixture.
When Should I Use Unsanded Style Grout?
Unsanded grout adheres better to vertical surfaces, so it is best used for wall tiles. You should also opt for non-sanded grouts if you are setting tiles with joints less than 1/8 inch in width.
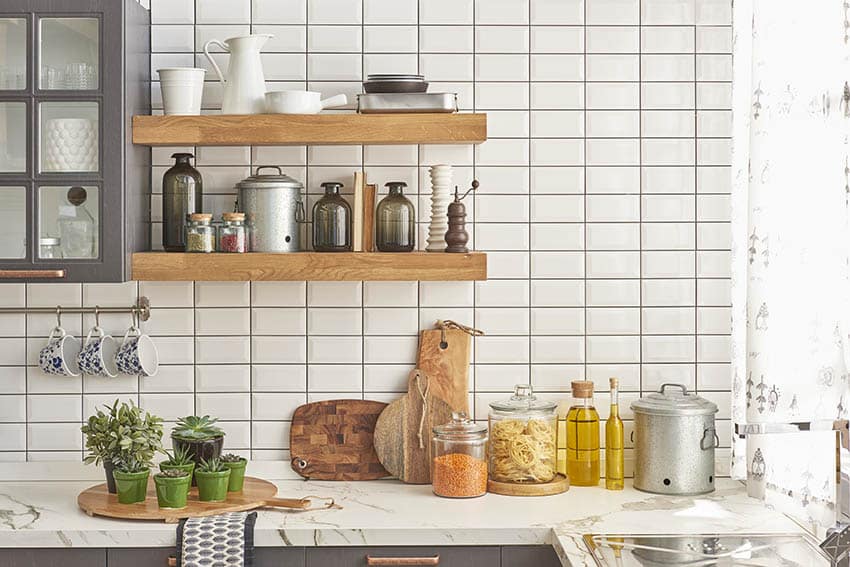
The most common application for unsanded grout is a kitchen backsplash or shower wall. If you are installing tiles that are easily scratched, like marble, for example, you should go for non-sanded grouts. Sanded applications may damage this type of tile. Unsanded mixtures have a less abrasive and much smoother texture, making it better suited for use for delicate tile surfaces.
Unsanded grout is also less solid than sanded and can crack or break under pressure, so you should not use non-sanded applications for floor tiles.
For more related designs, take a look at our article about tile patterns.