How to Choose Office Chair Dimensions: Size For Comfort

Those who run businesses recognize the value of getting the “ideal” office chair dimensions for themselves and everyone in their organization. A well-fitted desk chair can contribute to work productivity by providing a platform that hugs and supports the body, optimizing physiologic functions, reducing the risk of back injuries, and promoting optimal health in the workplace.
Although it is nearly impossible to customize office seating for each person in a large company because of budget constraints, most workplace seat furnishings have standardized sizes and adjustable features to accommodate individual needs.
Nevertheless, purchasing managers can work with occupational health and safety officers to appreciate standard office chair dimensions and compare them with individual employee requirements.
Standard Office Chair Size
No “standard” dimensions exist for office chairs. Manufacturers work with “principles” to create the best design for accommodating “most” employees. Brands emphasize a universal yet “modifiable” style, ensuring optimum occupational performance and wellness in the workplace.
Desk Chair Dimensions

Office chairs (also called desk chairs) are the quintessential workplace furnishings, allowing employees to perform their duties as comfortably as possible.
Seat Depth
Like any furniture product, a desk chair comprises different components with varying dimensions. For example, the seat’s depth (front-to-back span) can be as “shallow” as 16 inches (about 41 centimeters) to as “deep” as 22 inches or 59 centimeters.
Although most seats have these measurements, some brands might offer designs with “shallower” or “deeper” seat depth dimensions.
Organizations must recognize and appreciate seat depth’s value in promoting employee well-being and productivity. Too shallow, and employees could strain their pelvises, increasing the risk of low back pain.
It can also stress the legs by shifting the body’s center of gravity forward. Too “deep,” and office workers might experience postural issues.
Seat Width
Most desk chairs feature a sideways span of 19 to 21 inches or about 48.2 to 53.4 centimeters. American men have an average waist circumference (the “wraparound” measurement of the waist) of 40.2 inches or 102.1 centimeters.
Halving this value and considering the body’s side measurements show that 19 to 21 inches is “just right” for the average office employee.
Width is a crucial seat metric, allowing employees to “sink” their buttocks squarely into the cushiony platform. Ideally, office managers must ensure the product accommodates the person’s bottom without sections extending over the edges.
Sadly, some employees have a “wide” girth, making sitting on a standard size “uncomfortable,” especially those with armrests. It’s important to get the measurements right to avoid discomfort.
Armrest Height and Width
Standard desk chairs feature 2- to 4-inch-wide (about 5 to 10 centimeters) armrests, allowing employees to rest their forearms as comfortably as possible. Meanwhile, desk chair armrests typically rise 5 to 8 inches (about 12.7 to 20 centimeters) from the seat surface.
Most moels feature armrests on both sides of the seat, allowing users to rest their elbows and forearms, releasing unnecessary tension from the shoulder and upper back.
Headrest and Backrest
Most desk chairs are 12 to 19 inches from side to side (about 30.4 to 48 centimeters) and 18 to 22 inches from the seat’s surface to the backrest’s topmost edge (about 45.7 to 55.8 centimeters).
Meanwhile, desk chair headrests are 5 to 6 inches tall (about 12.7 to 15 centimeters), sufficient for accommodating the bony prominence at the back of the head.
Although backrest design varies across brands, they must accommodate the user’s back, especially the midsection, where the spine’s outward curvature is more prominent.
Office managers look for products with a slightly concave backrest to nestle the body’s natural contours. Some do not have headrests, but most do. This feature allows users to rest the back of their heads, reducing neck tension and stress.
Chair Base
Ideally, the base must be wider than the seat to ensure stability and balance. Hence, purchasing officers can expect a standard desk chair to feature a 22- to 24-inch-wide anti-tilt stability base (about 55.8 to 70 centimeters).
Dimensions of a Desk Chair by Height
User height is crucial for choosing the correct office chair unless the furniture has adjustable components (i.e., seat height and depth). Although width and depth have more or less “standard” ranges, seat height depends on the individual user’s height.
For example, employees “shorter” than 5 feet should opt for a 15.9-inch (40.2-centimeter) tall office chair. On the other hand, a worker standing 5 feet 6 inches will find a 17.8-inch-tall office chair more comfortable and conducive to work (about 44.9 centimeters).
Here’s a rundown of dimensions purchasing officers must observe when buying seating based on employee height.
| User Height | Office Seat Height |
| <5 feet or <149 centimeters | 15.9 inches (40.2 centimeters) |
| 5.0 to 5 feet 6 inches or 151.5 to 166.5 centimeters | 16.2 to 17.8 inches (40.9 to 44.9 centimeters) |
| 5 feet 7 inches to 6.0 feet or 169 to 181.5 centimeters | 18 to 19.4 inches (45.6 to 49 centimeters) |
| 6 feet 1 inch to 6 feet 6 inches or 184 to 196.5 centimeters | 19.7 to 21 inches (49.6 to 53 centimeters) |
| >6 feet 6 inches or >196.5 centimeters | 21 to 21.6 inches (53 to 54.4 centimeters) |
What is the Correct Chair Height for a Desk?
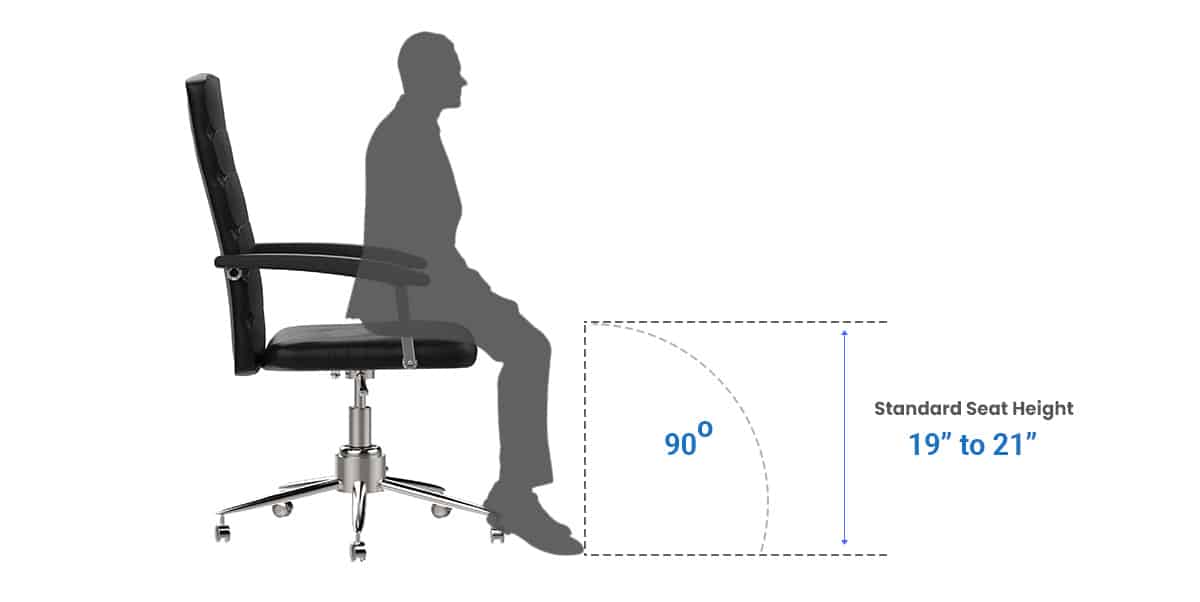
The “correct” desk chair height is relative, often depending on the user, specifically leg length. Ergonomists describe the ideal posture as allowing users to plant their feet firmly and squarely on the floor while maintaining a 90-degree angle at the knees.
This description requires the user’s thighs to be parallel to the floor, with the leg in a vertically straight position.
Hence, a 19- to 21-inch seat height is standard for conventional office chairs. However, manufacturers recognize user individuality, knowing some users have longer lower limbs than others. And that is why most products now feature fully adjustable heights.
Executive Chair
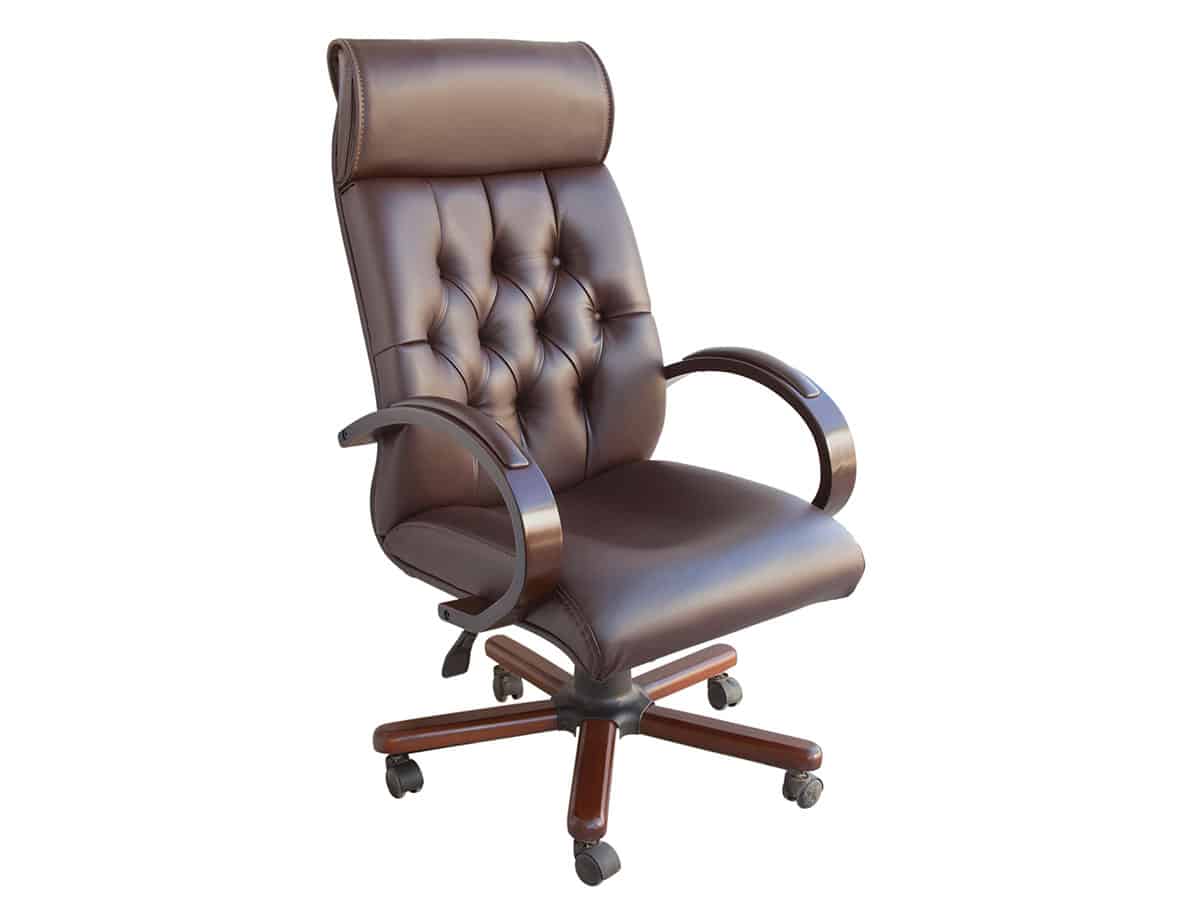

One can expect the seat of an executive chair to be slightly wider (Generally over 21 inches or 48 centimeters) than the average employee-use furniture. Seat height, depth, armrest measurements, backrest dimensions, and headrest metrics should be identical unless custom-built.
Standard Executive Chair Dimensions:
| Feature | Measurement (inches) | Measurement (cm) |
|---|---|---|
| Overall Height | 44 – 52 | 112 – 132 |
| Width | 25 – 30 | 63.5 – 76.2 |
| Depth | 20 – 24 | 50.8 – 61 |
| Seat Height | 17 – 22 | 43.2 – 55.9 |
| Backrest Height | 25 – 30 | 63.5 – 76.2 |
| Seat Width | 19 – 23 | 48.3 – 58.4 |
| Armrest Height | 7 – 9 | 17.8 – 22.9 |
These furnishings feature elements standard seating products do not have. For instance, executive chairs have premium-quality upholstery, revolving seats, ample cushioning, and heavy-duty metal frames.
Most executive chairs have leather materials, spring-loaded seats, high-quality foam fill, and top-notch fabrics (i.e., chenille).
These products are generally “larger” than traditional sizes, affording senior managers and organizational leaders maximum comfort. These furnishings have excellent lumbar support and superior durability, allowing executive-style products to last for decades.
Ergonomic Chair Measurements

Ergonomic chairs look like ordinary seating but have several advantages. First, these furnishings feature adjustable elements to ensure a user-specific back and armrest configuration for optimum ergonomic comfort and work productivity.
For instance, some ergonomic office chairs feature an adjustable seat depth. It allows users to modify the traditional 16- to 22-inch seat depth to suit their needs.
Most units have adjustable armrests, backrests, headrests, seat height, and seat tilt. These features empower users to ensure optimum comfort during work.
Second, ergonomic products have exceptional lumbar support, with some models allowing customization to match the user’s natural spinal contour.
Eames Chair Sizing

The Eames chair is perfect for mid-level executives, although some top honchos also use it for its formal style and plush comfort. Its 26.5-inch (or 67-centimeter) right-to-left span can accommodate even “oversized” leaders, managers, and supervisors, giving them sufficient room to wiggle about without feeling cramped.
Its seat depth is also adequate for big bosses at 29.5 inches or about 75 centimeters. Meanwhile, the armrests support the forearms and elbows at 23.5 to 25 inches (about 60 to 63.5 centimeters) from the floor surface.
Resting one’s body on an Eames recliner is easy and comfortable because of the furniture’s uniquely inclined design. It has a natural tilt that cradles the back, ensuring users will not experience discomfort or pain.
What is the Minimum Size for a Chair?
The smallest office chair depends on the person. For instance, it is not unusual for a 4-foot, 11-inch employee (149 centimeters) to find a 15.9-inch-high (40.2-centimeter) seat ideal for such a “stature.” Unfortunately, giving this same item to a 6-footer will create back problems and discomfort.
Some brands offer products with 14-inch seat heights. As for the width and depth, the minimum product has measurements at the lower end of the size range (perhaps even lower).
What Size Chair Do I Need?
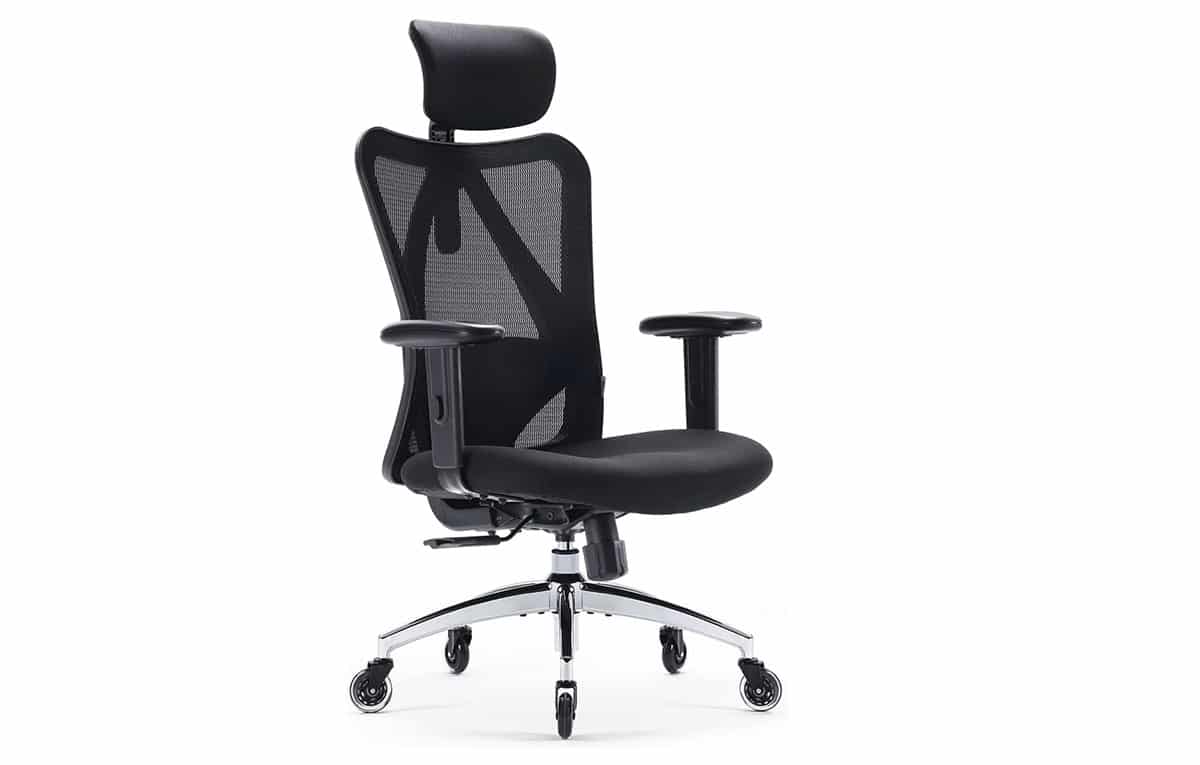

Office chairs do not come in a universal size if one expects optimum comfort. Users must consider their body measurements to determine the “ideal” size.
However, pointers exist to make buying decisions more spot-on.
• The seat height should be 10 inches lower than the desk height or any work surface.
• The seat depth should allow for a 1.5-inch (4-centimeter) allowance from the seat’s front edge to the back of the knee, with the back firmly pressed against the backrest.
• The seat width must accommodate the body’s cross-section, measured at the hips’ widest points.
• The backrest should not be lower than the shoulder blades and wide enough to accommodate the whole back, including the shoulders.
• The headrest must not be higher than the head’s lower back.
• The armrest must allow for a 90-degree angle at the elbows.
Other Buying Considerations
Regarding the design features, there are a few other considerations. For one, it is important to look for products that offer the proper legs, wheels, or casters for the type of floor you have. A rolling functionality with the right flooring will increase productivity and allow you to reach things within the office.
Another consideration is the overall construction and durability of the product. You may want a light-duty or heavy-duty product depending on the amount of space you have, your budget, and your desired weight capacity.
You may need the ability to swivel in your seat, which can be productive for those with l-shaped desks or for ease of entering and exiting the workstation.
It is also necessary to consider the amount of cushion and overall fit of the seatback. For this, you may need to physically test out the product in a store to get a feel for how it’s upholstered and its available adjustments.
For more information and answers to popular questions, visit our desk types guide.