Types Of Furnaces (Styles & Benefits)
In this guide you’ll see the different types of furnaces including their styles, benefits, efficiency, cost, and tips on how to choose the right furnace for your home. We will also provide tips on how to choose the right furnace for your home, taking into consideration design, materials, and construction experience, ensuring you select the best heating solution for your specific project.
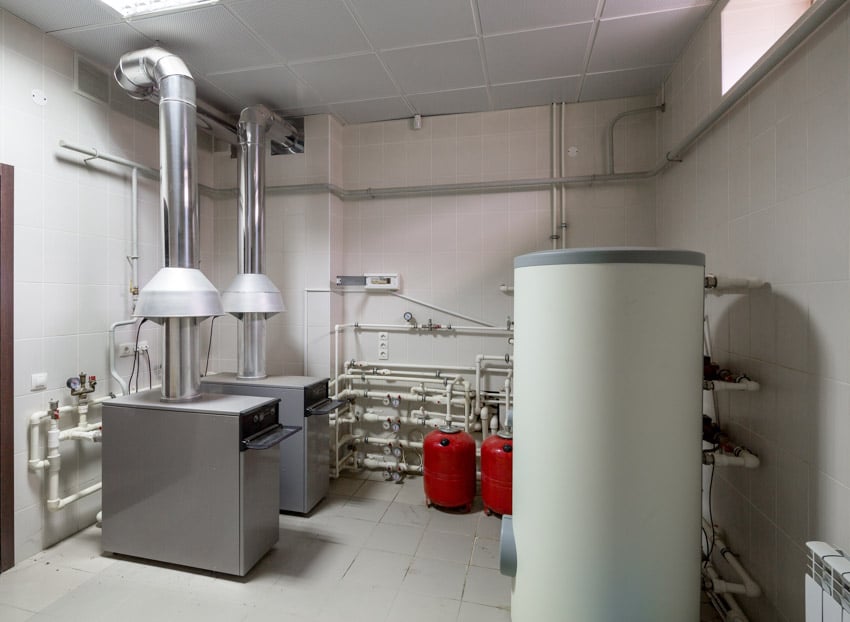 Whenever the temperature falls, your furnace kicks in to make you pleasantly warm. Indeed, your furnace is the source that drives your home’s heating system, but keep in mind that it is not a one-size-fits-all unit.
Whenever the temperature falls, your furnace kicks in to make you pleasantly warm. Indeed, your furnace is the source that drives your home’s heating system, but keep in mind that it is not a one-size-fits-all unit.
The operation of different types of furnaces varies, with factors like design, construction and materials playing crucial roles in their construction and performance.
This article will lead you through the various types of furnaces, how to select the correct one for your home and other valuable information about furnaces. We’ll also discuss the impact of your previous experience with heating products and the role this may play in determining the best choice for your project. [toc]
What Is A Furnace?

Indeed, a furnace is a component of the HVAC system (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning). Whenever you use a regulator to adjust the temperature of a room, you normally turn on the furnace.
The air in the space may be colder than the temperature you set on the thermostat after making a temperature adjustment. This causes the fan to activate, the furnace to turn on, as well as the air to heat up and circulate around the room. Once the air temperature drops below the thermostat setting, the cycle gets repeated.
A furnace does more than just activate a blower to warm the air, though. To guarantee that the air is properly warmed up before it leaves the unit, several mechanisms are applied.
Nonetheless, there are different types of furnaces. And although the fundamental operation of these types is the same, they still have distinctive features, costs, and efficiency rankings, as well as unique design and material considerations.
Single Stage Furnace
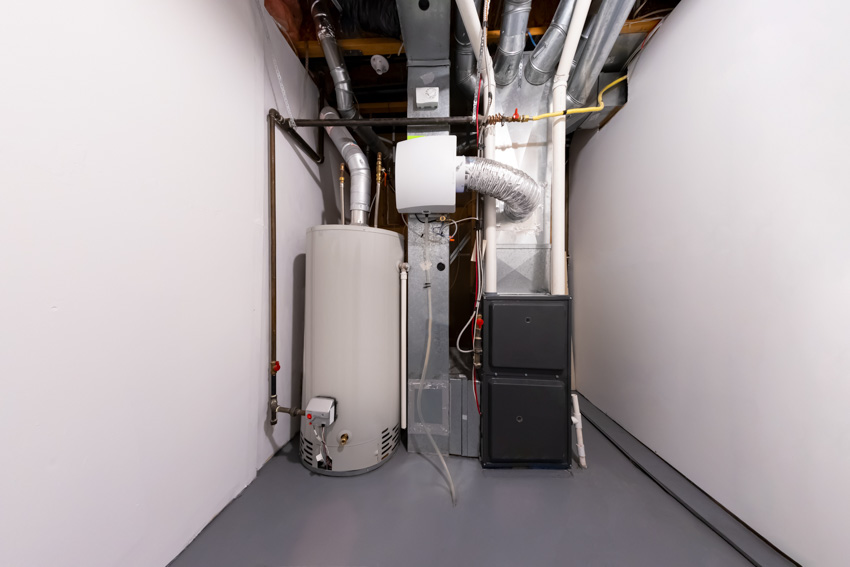

Single-stage furnaces contain only one heat output stage – high. Nevertheless, this type of furnace can be quite expensive for your wintertime energy bills because every time your furnace switches on as it disperses the most significant amount of energy it potentially can.
Benefits
• Due to the simplicity of its structure, this furnace type is the most affordable to acquire.
• A single-stage furnace is typically sufficient for heating a small to the medium-sized, single-story house.
Efficiency: When it pertains to heating a huge or multi-story house, a single-stage furnace may not be that efficient. Since the furnace operates at full capacity whenever it is turned on, the spaces surrounding the vents will heat up rapidly.
Although the remainder of your house’s temperature catches up, your thermostat may assume your entire house has attained your targeted temperature and turn off the furnace abruptly.
This causes hot and cold zones in your house, which can be affected by the choice of heating system or even factors such as air ducts and ceiling height.
Homeowners will explore different options to avoid cold areas, like boosting the target temperature on their thermostats so that the furnace does not switch off so prematurely. Even though this solves the problem, it introduces another – costlier energy expenses due to increased usage.
Cost: The single-stage furnace alone typically costs $1,000 to $1,500, with labor costing another $1,000 to $2,000. Factors such as the choice of contractors and the title of the furnace model can also impact the price. High-efficiency models might cost up to $4,000 to purchase and install.
Variable Speed Furnace
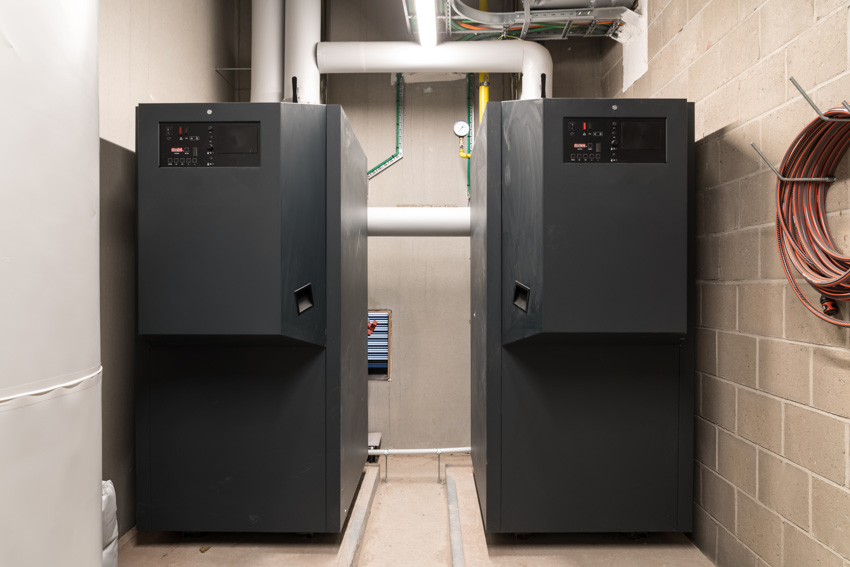

The fan motor in variable speed furnaces can operate at varying speeds to manage the amount of hot air distributed around the different types of rooms in a house, taking into consideration factors like air ducts and ceiling height.
Improved ventilation leads to a more pleasant atmosphere in terms of both humidity and temperature. Additionally, many of the variable speed furnaces on the marketplace are among the most sophisticated options in the industry.
Although they may be slightly more expensive upfront, the reductions in energy expenses throughout the lifespan of the equipment are easily appreciated.
Benefits
• A variable speed furnace’s motor can continuously run to keep your home’s air circulating even if the furnace is not turned on.
• Because your air is consistently flowing through the filtration system in your HVAC unit and then being cleared of germs, pathogens, as well as mold spores, this function promotes cleaner and healthier indoor air quality.
Efficiency: Because air is constantly being circulated throughout your house, this superior control over airflow might eliminate the need for the furnace to work very frequently. This can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower monthly electricity bills.
Cost: The price of a variable speed furnace ranges from approximately $2,000 to $5,000. Although this may appear to be a hefty cost to pay, the unit’s efficiency will indeed provide an incredible return on investment over time.
Electric Furnace
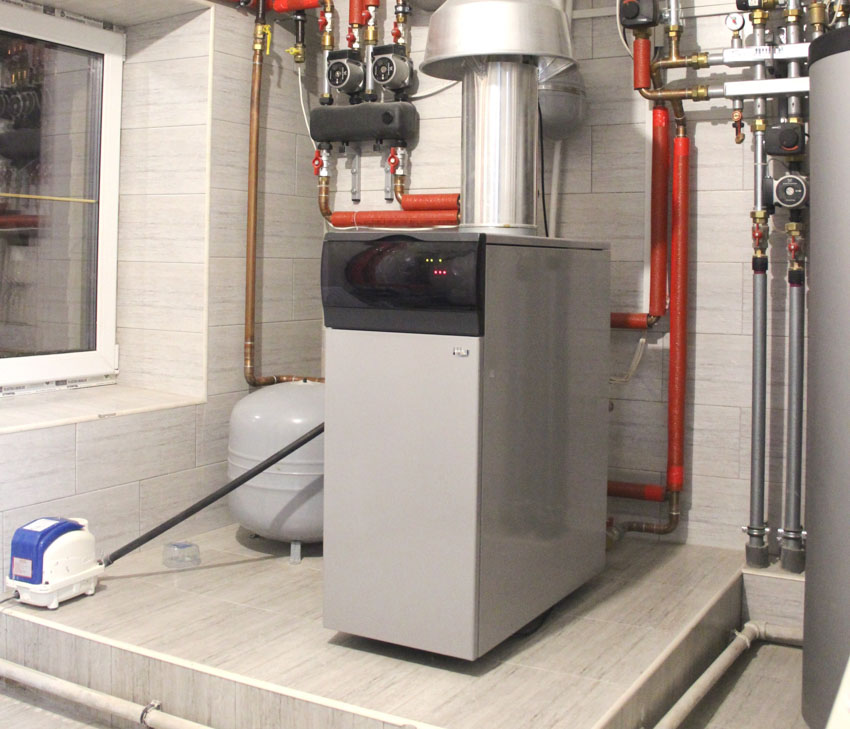

Electric furnaces are typically less costly to install and smaller in size than other furnaces, making them easier to integrate into certain types of garages or basements.
The processes for an electric furnace are the same as those for a gas furnace. When the temperature falls below the temperature established on the thermostat, the system switches on.
An electric furnace is distinguished by the application of an electric motor to push air through and away from the furnace.
When the air temperature falls below the minimum, the coiled parts of the wire generate electric currents that heat the electric heater. The air is forced over the heating components through a filtration system and out into the surroundings by a fan.
Benefits
• The standard electric furnace is a very long-lasting option, which can be inherited by your upcoming family generations, making it a popular choice among homeowners looking for reliable heating solutions.It normally lasts 20 to 30 years, serving as a reliable energy source during this time.
• An electric furnace does not emit dangerous gasses such as carbon monoxide and operates at various temperatures, providing both heating and cooling functions.
• There is no dust or ash to bother when using an electric furnace as there is no combustion, making regular maintenance and access convenient.
Efficiency: Since there is zero fuel consumed, all electric furnaces obtain an Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) value of 100%. The impressive AFUE rating is owed to the unique energy sources they use.
Usually, electric furnace types use a heat-releasing technique that does not dry the air as quickly as a gas furnace does, allowing your indoor humidity levels to remain consistent and pleasant.
Cost: The costs for a basic electric furnace can vary from $900 to $1,500. A high-quality electric furnace, on the other hand, might cost between $1,500 and $6,000.
Total expenses vary depending on localized labor rates, fuel source, brand selection, and a few other considerations. Electric furnaces, nonetheless, have higher operating expenses than gas furnaces.
Natural Gas Furnace
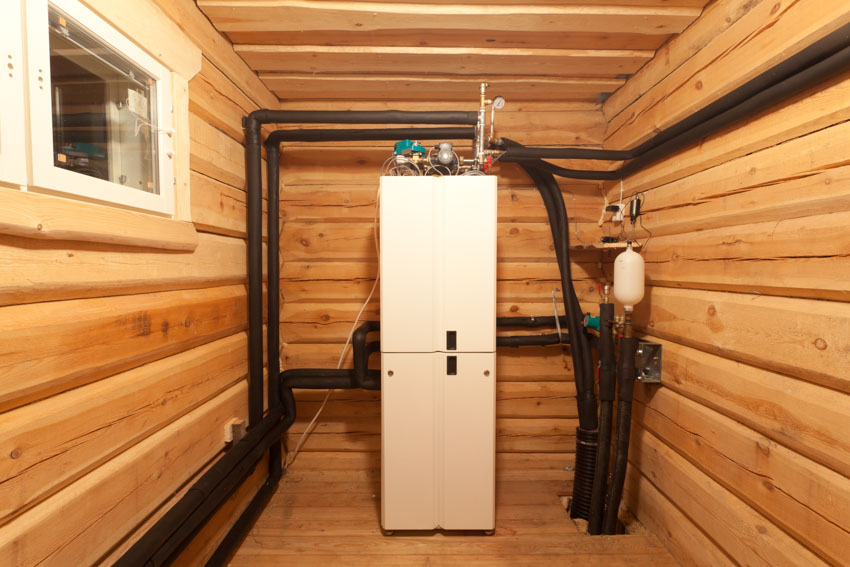

This boosts the temperature of air circulated by fans through the ducting. Gas furnaces provide consistent heating and are inexpensive to operate due to the low cost of gas and the ability to adjust temperatures efficiently.
Inside the combustion zone of a natural gas furnace, high-quality air is kept separate from low-quality waste. The heated air is then discharged into the environment. Once the air cools, it is forced into the furnace and reheated in a similar manner.
Benefits
• If your power goes out, you may still heat your home using a natural gas furnace, keeping you cozy while you are waiting for the power to return.
This is not only crucial for your pleasure but is also a good preventative measure for your home plumbing system, ensuring proper access to both heating and cooling.
• Natural gas is often less expensive than any other fossil fuel for residential heating. This is achieved due to the efficiency of modern natural gas furnaces and their effective fuel source management.
Efficiency: The vast majority of natural gas furnaces can be up to 98% efficient, resulting in the lowest possible projected heating bills.
Plus, natural gas produces almost minimal carbon monoxide when used in a correctly maintained and working heating system, serving as one of the better energy sources and temperature regulators.
Cost: The usual installation cost for a natural gas furnace is around $3,000 to $10,000, while a high-efficiency type, or combination heater & air conditioner unit may cost more. These versions are more expensive, but you will save money on energy expenditures over time.
Modulating Furnace
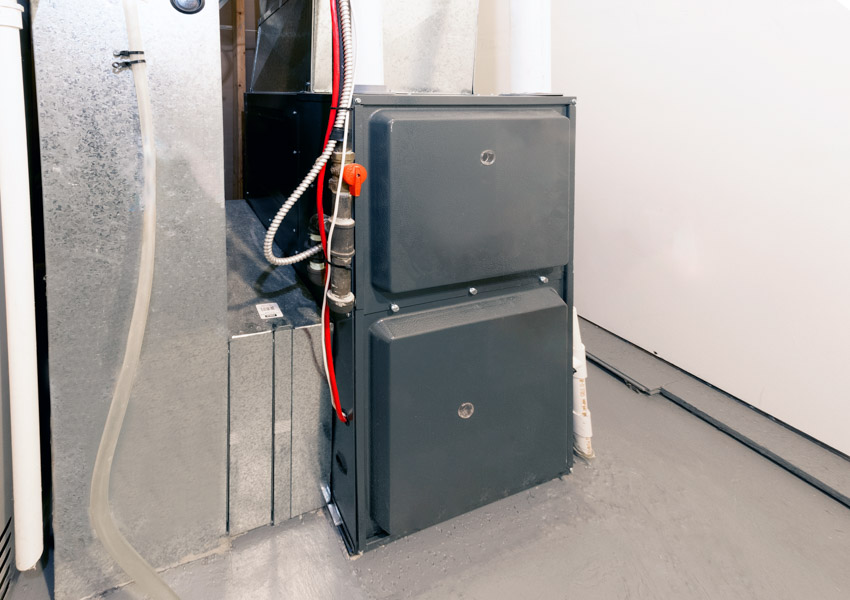

Whenever you use a modulating furnace, both the gas valve and the compressor fan are continuously changing to maintain the temperature you want inside your home, ensuring easy access to various temperature settings.
Benefits
• Modulating furnaces work optimally at maintaining a constant temperature around your home since there are quite many settings accessible. These furnaces often include a heat exchanger, which helps in regulating the temperature.
• Modulating furnaces typically spend a significant amount of time working at an extremely low setting. This entails using reduced fuel and lowering the fan setting. For budget-conscious homeowners, the reduced energy consumption serves dual purposes – saving on utility bills and being eco-friendly.
A lower fan setting indicates that air is moving at a reduced pressure throughout your system. Slower air movement usually enhances the efficiency of your furnace filter and the quality of your indoor air.
Efficiency: Modulating furnaces are more energy-efficient and have better temperature regulation than single-stage furnaces. Modulating furnaces can contain a multitude of stages and are very customizable.
Additionally, installation costs for these furnaces may be higher initially, but the long-term energy savings make it a worthwhile investment.
Using this type of furnace, you can prevent short-cycling your system, which reduces fuel consumption and stress on the furnace. This offers long-term savings in all places: reduced bills, minimal maintenance, as well as a furnace that lasts longer.
Cost: Modulating furnaces are not that affordable, with prices ranging from $5,000 to $7,500 for both acquisition and installation. Nevertheless, because of its lower operating costs, a modulating furnace can eventually compensate. To begin with, switching to a modulating furnace eliminates the need to maintain an outdated furnace, therefore decreasing maintenance expenses.
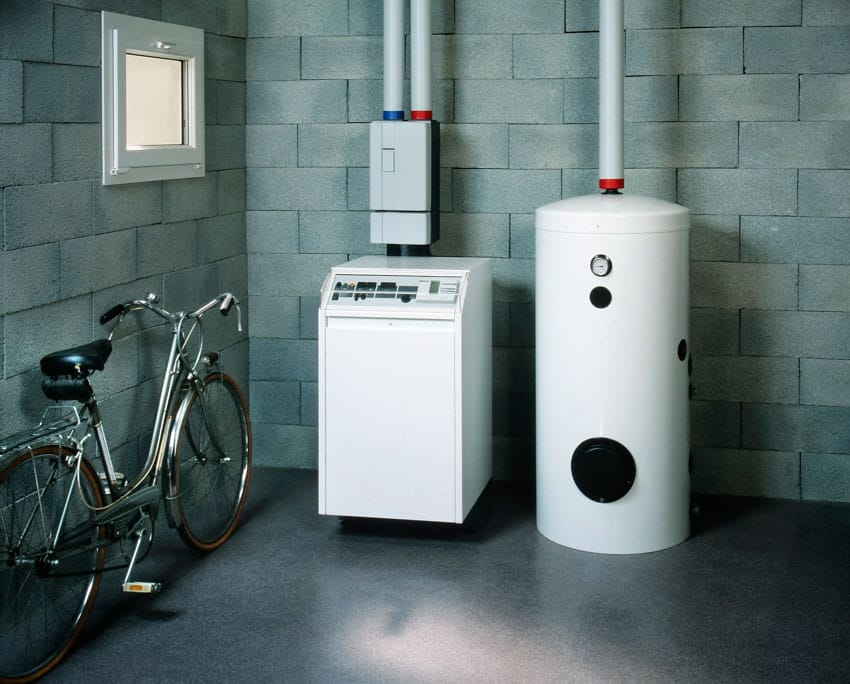
Propane Furnace

Benefits
• Propane furnaces have a lengthy lifespan, lasting around 15 to 20 years. They can, nevertheless, endure even longer if properly cared for.
• They are also simple to maintain because propane burns cleanly. You will not be bothered about soot or overheated electrical components with these furnaces.
Efficiency: A propane furnace is a low-energy furnace that works on propane gas. These furnaces are mostly recommended by experts since they outlast most types of furnaces in terms of endurance, cost-efficiency, and simplicity of use. A high-efficiency propane furnace has an efficiency rating of 90 to 98%.
Cost: The cost of setting up a propane furnace varies based on the size, quality, size of your propane tank & house. A low-end propane furnace costs about $2,200 on average in the United States. A regular propane furnace, on the other hand, costs roughly $4,000, whereas a high-efficiency furnace costs around $5,800.
Oil Furnace
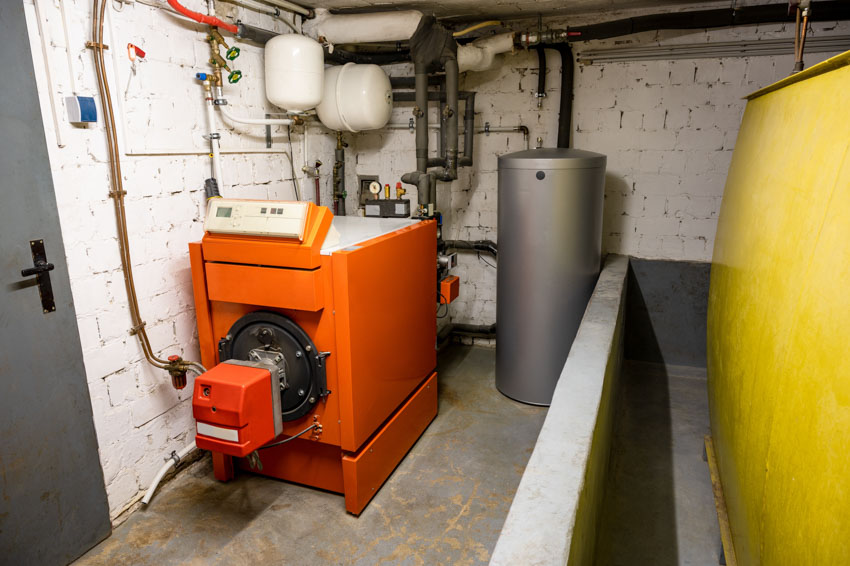

As it passes over the heated burning chamber, the air that is going to be released into the house at the finish of the procedure heats up. The air is then discharged back into the atmosphere after the process of passing over the chamber is completed.
Benefits
• Oil is biodegradable, toxic-free, and free of cancer-causing substances. In reality, oil furnaces are among the cleanest methods of burning. Modern oil burners emit very little smoke or flammable discharge.
• Oil is a non-explosive resource that will not burn unless it is geared up to 140 degrees, therefore there is very minimal possibility of it igniting. Whenever an oil furnace seems to malfunction, it will generate straightforward warning signs such as smoke, smells, or soot.
Efficiency: Oil furnaces produce the fiercest flames, which implies that oil heats your house more quickly while using less fuel. Oil produces more heat per unit of energy than other sources. Switching to a high-efficiency furnace can boost the efficiency of your heating system by 28 to 30%.
Cost: For the unit itself, the usual oil furnace costs around $500 to $2,500. The cost of an oil furnace varies according to size, manufacturer, and energy efficiency. The average overall installation cost will be roughly around $5,700 to $6,000.
Wood Burning Stove
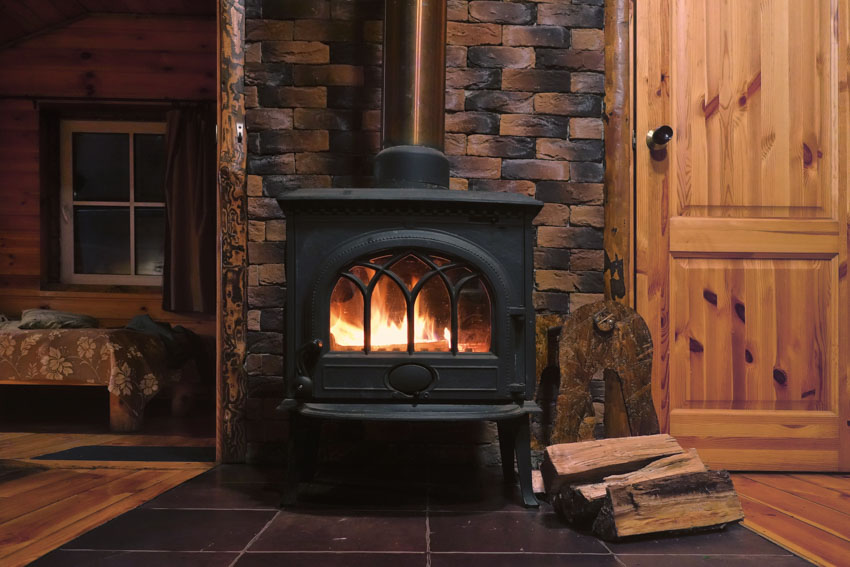

Indoor versions with stunning glass firebox doors that resemble fireplaces are also available. Fans, duct work, and heat converters are also used in a wood-burning stove furnace to transfer heat.
Benefits
• You must have a consistent supply of wood if you operate a wood-burning furnace. Fortunately, a lot of manufacturers provide efficient wood transportation services to make this simpler, which makes it beneficial to your wood-burning furnace maintenance.
• In comparison to other forms of heating systems, today’s modern wood-burning furnaces are incredibly efficient and can lead to significant savings.
Efficiency: Wood-burning furnaces are approximately 70 to 80% efficient. These furnaces also have lower operating costs than standard gas and electric furnaces.
Furthermore, because wood is a renewable and long-term resource, wood-burning stone furnaces are ecologically friendly. EPA-certified devices emit the fewest pollutants and have the least potential to harm the environment.
Cost: The cost of installing wood-burning stove furnaces ranges from approximately $1,500 to $5,000.
How To Choose A Furnace

• The size of a furnace varies. Picking the correctly sized furnace is not quite as simple as it seems; the size is determined by how large the space is, how high the ceilings are, as well as other minor considerations.
• The type and size of the furnace you must purchase will be influenced by the location of the space.
• The type and size of a furnace are also affected by the surrounding climate, so you should be knowledgeable about the usual climate in your region.
• You must be aware of how much it will cost you in the coming years to maintain and repair the furnace.
• Inquire with the professionals about any issues that may arise as a result of using a furnace.
Furnace Placement
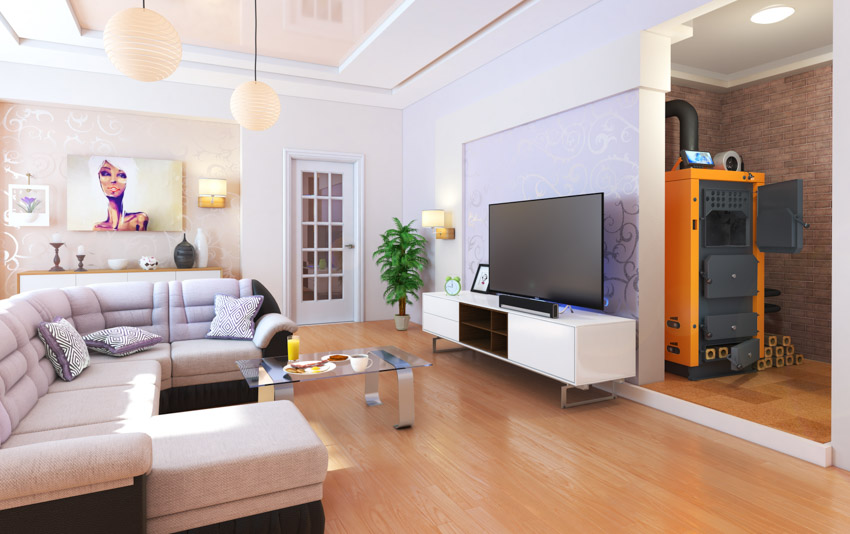

• Garages: Most types of furnaces are installed in garages. The garage in numerous modern homes is constructed with a specific recess that stores the furnace without compromising parking space.
• Huge Laundry Rooms: Furnaces and other significant types of appliances should not coexist in such a little space. Nevertheless, in bigger houses, the furnace may be installed in a massive laundry room.
• Attics: The furnace can be placed in the attic crawl spaces in houses that have space constraints.
• Utility Spaces: Some houses, particularly those without the garages or basements, have a separate space in the central core of the home that can accommodate the furnace.
What Size Furnace Do I Need?
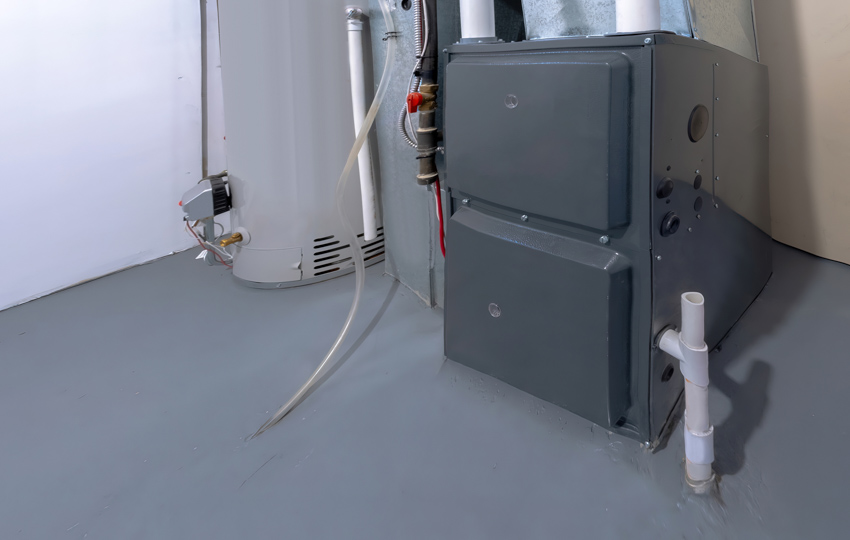

(BTU – British Thermal Unit – a heat measurement unit) However, climate zones can assist you in determining how many BTUs per square foot you will need for your home.
How Long Do Furnaces Last?

How Much To Replace A Furnace?
The cost of replacing a furnace can range from $3,000 to $9,000 as it will depend on the type of furnace you own, the size of your house, the efficiency of your replacement furnace, as well as the complexity of the technology. This involves not only equipment expenditures but also labor and licensing charges.
Heat Pump Vs Furnace
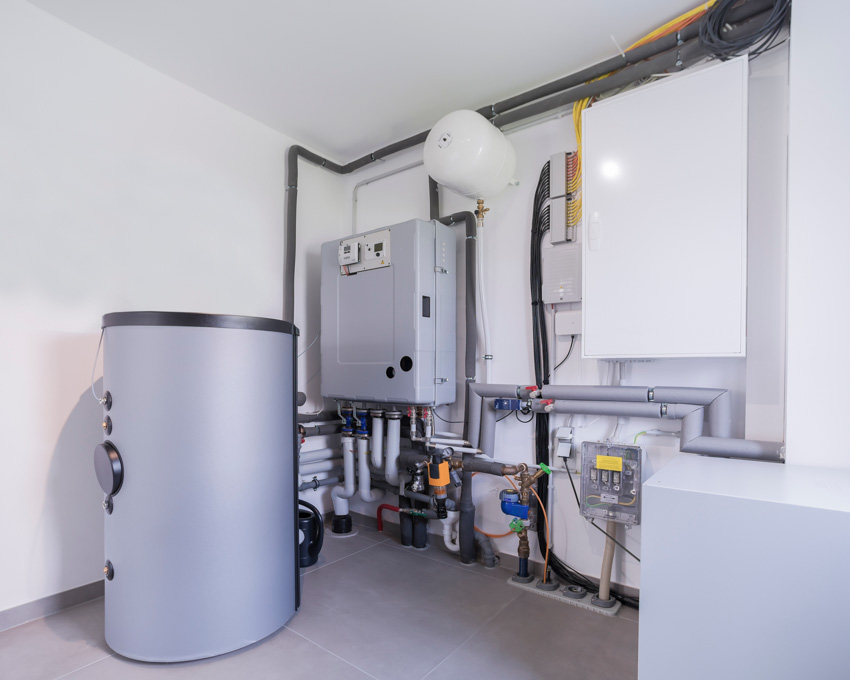

In Terms of Efficiency: It is difficult to compare the energy efficiency of the different types of furnaces and heat pump units. Heat pumps are scientifically more energy-efficient than furnaces given their ability to transmit more energy than they need, but furnaces are more efficient in terms of keeping your interiors warm.
In Terms of Maintenance: Regular maintenance will help heat pumps and furnaces survive longer and run more effectively. These systems feature air filtration systems that can be simply replaced by the vast majority of homeowners.
A conventional residential heat pump system consists of an outdoor unit as well as an indoor unit that should be maintained and examined once a year. A standard furnace does not usually necessitate an outdoor unit, but it is frequently used in conjunction with a centralized air conditioning system.
In Terms of Space Consumed: Most types of furnaces are normally placed indoors and necessitate at least 30 to 35 inches of clearance throughout all sides. A heat pump just needs 24 to 27 inches of clearance and is normally installed outside.
A conventional air-source heat pump system, on the other hand, necessitates an indoor air processor device known as a fan coil.
See more related content in our article about the different whole house humidifier pros and cons on this page.