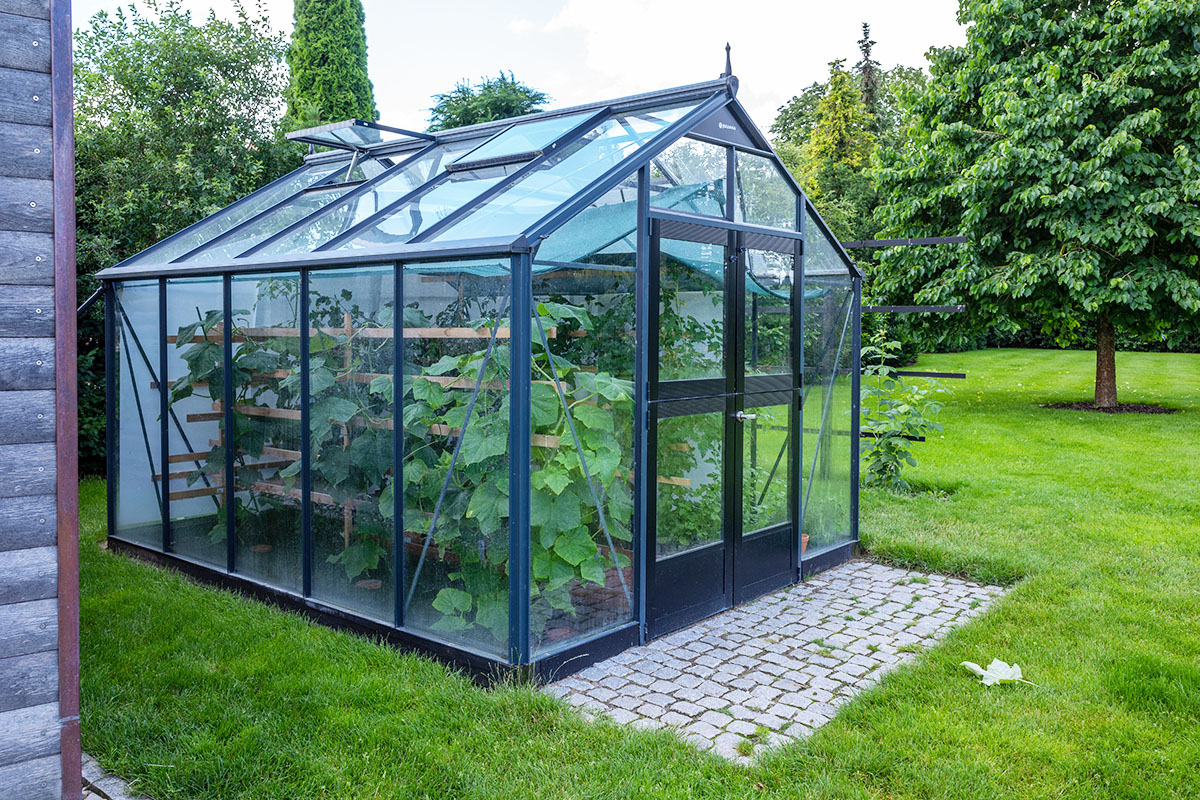
Greenhouse Sizes (Average, Small & Family Dimensions)

More and more families are embracing sustainable backyard farming, allowing them to grow food for self-sufficiency. The idea is to produce higher yields amidst space limitations. Unfortunately, traditional backyard farming or gardening poses many challenges. Controlling environmental factors (i.e., wind, sun exposure, temperature swings, and pests) is never easy. Thankfully, greenhouses exist to help families achieve food self-sufficiency and monetary savings.
A thoughtfully-planned and well-constructed greenhouse empowers families and individuals to protect plants against harsh weather, pests, and other yield-reducing factors. These structures will have food all year round, flowers to sell even in the off-season, and enjoy the many health benefits of backyard farming or gardening.

Upload a photo and get instant before-and-after room designs.
No design experience needed — join 2.39 million+ happy users.
👉 Try the AI design tool now
Constructing a greenhouse in the backyard is not complicated. Homeowners can complete the project with a fundamental understanding of what plants need to grow and thrive. Perhaps the most important question homeowners have relates to the greenhouse’s size. This article addresses these concerns by exploring different green house sizes.
Average Greenhouse Dimensions
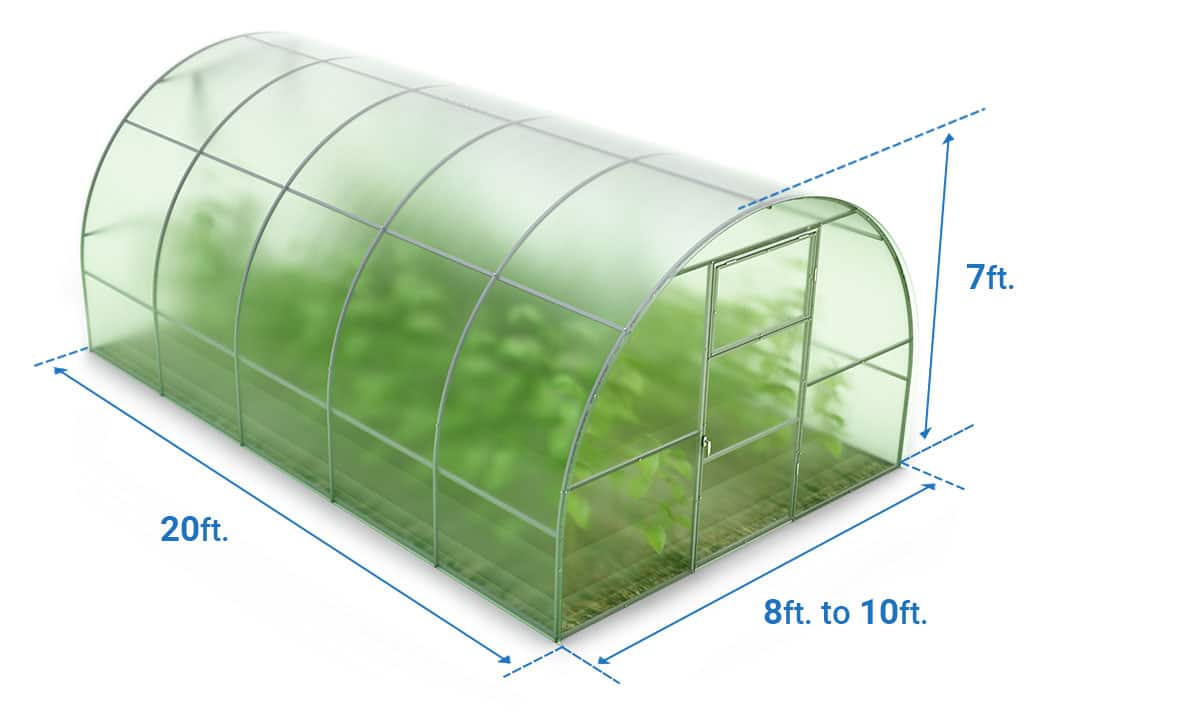
Installing a greenhouse on one’s property involves deciding between a prefabricated unit and building one from scratch. Most families prefer the former because it is less laborious. They could clear a space in the backyard, buy the pop-up structure, and set it up.
On the other hand, DIYers opt for custom-built greenhouses, allowing them to create a climate-controlled ecosystem for their plants based on their needs. Although they have three crucial dimensions, width is the most vital. Conventional hobby structures or backyard units span 8 to 10 feet (2.44 to 3.05 meters) from side to side.
This measurement is enough for two to three rows of plant beds or planter boxes. The space in the middle is sufficient for gardeners to move about.
As for the greenhouse’s length, families can choose 20 feet (6.1 meters) as a good starting point. Commercially-available pop-up structures vary in length in 2-foot (about 61 centimeters) increments. Hence, one cannot find a 21-foot-long (6.4 meters) structures, only 20 or 22 feet (6.1 or 6.7 meters).
The growing structures height also matters, with the average at 7 feet or 2.13 meters. It is worth noting that some families pick shorter buildings to accommodate certain plants. The structures height influences how well plants grow. So homeowners might want to learn the maximum heights of their chosen plants to avoid overcrowding and stunting their growth.
Examples of Greenhouse Room Sizes
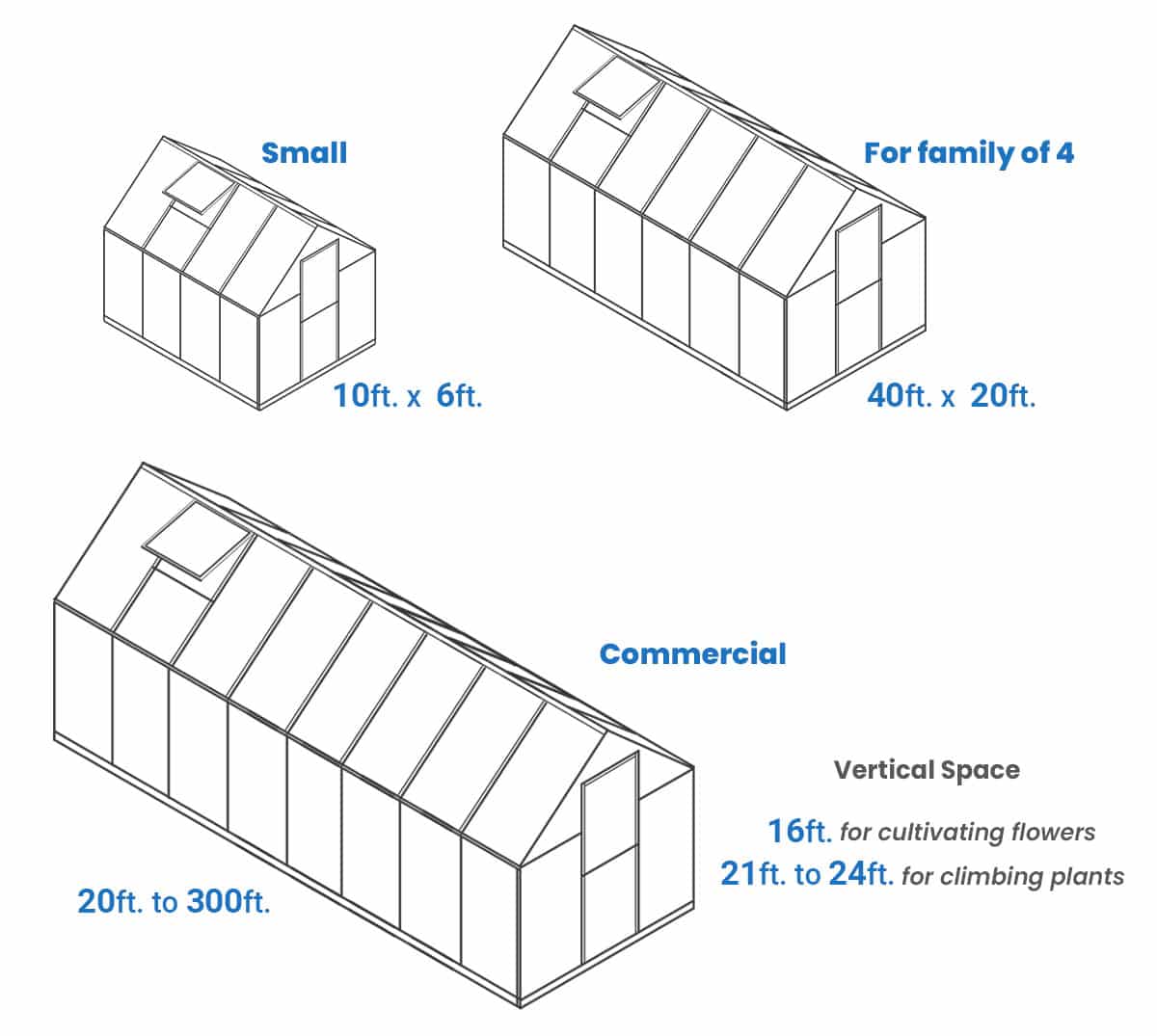
Small Greenhouse Sizes
Families who want to protect a small garden plot or a seedling bed can pick a mini greenhouse. The smallest on the market has a side-to-side span of 71 inches (1.8 meters), a front-to-back measurement of 36 inches (91.4 centimeters), and a height of 36 inches. Some designs might have a taller but narrower construction, allowing gardeners to stack planters. Such a design is perfect for homes with limited space but still want to benefit from backyard gardening.
Most families with tight spaces will do well with a mini greenhouse. However, households with sufficient backyard space can opt for a small 6-foot-wide building (1.83 meters). These structures are enough to grow carrots, peppers, tomatoes, herbs, and other crops to minimize grocery expenses on these ingredients.
As mentioned, length is variable. Nevertheless, small greenhouses are 10 feet (3.05 meters) long. One can always install two 6×10-foot units in the backyard to account for plants with different growth requirements (i.e., climate).
Size of Greenhouse For a Family Of 4
Families must realize that greenhouse sizes hinge on available space. They could buy a 12×30-foot (3.66×9.14-meter) structure, but it might not fit in a 300-square-foot (27.9-square-meter) backyard space. Hence, measuring the prospective site is essential, whether for a family of 4 or 10.
Still, most experts recommend an 800-square-foot (74.3-square-meter) growing space for a four-member household. This requirement assumes a 20-foot (6.1-meter) width and 40-foot (12.2-meter) length for the building.
The dimensions are sufficient for two 3-foot-wide (91.4 centimeters) aisles between four 3-foot-deep benches, enough to grow crops to feed a family of 4.
If such a project is not feasible, the family can opt for a 10-foot-wide (3.05 meters) space with two 3-foot-deep benches sandwiching a 3-foot-wide walkway or workspace.
Average Commercial Sized Greenhouse
Commercial growers observe no limits to the sizes of their greenhouses. These are massive structures covering hundreds of acres of farmland. These nursery structures maximize horticultural technologies to improve crop yield without incurring substantial expenses.
The minimum side-to-side span of a typical commercial greenhouse is 20 feet (6.1 meters), although it is not uncommon to see commercial growers build more expansive shelters. These structures can extend 300 feet (91.4 meters) from the entrance to the back of the growing space.
Commercial structure heights vary depending on the crops. For example, those that cultivate flowers and similar plants need a minimum vertical space of 16 feet (4.88 meters). On the other hand, climbing plants (i.e., vines) need 21 to 24 feet (6.4 to 7.3 meters) of ground-to-ceiling space.
What Size Greenhouse Do I Need?

Greenhouse sizes are relative. A homeowner might have a structure that is smaller or bigger than a neighbor’s. Variations in structure sizes are a function of individual preferences, backyard farming requirements, and other factors. Families who want to install one in their backyards should consider the following pointers to determine the ideal size.
• Local Regulations
Many aspiring greenhouse owners think installing such a structure in their backyards does not require securing any permit. Unfortunately, as culturally diverse as the United States is, so do local jurisdictions.
Although most jurisdictions (i.e., municipalities, cities, counties, and states) do not require a planning permit, some might. Hence, homeowners must check with their local administrators or zoning department for guidance, according to Arcadia Glasshouse. Moreover, contacting homeowner associations and similar organizations can help avoid legal entanglements.
Building and zoning ordinances can also influence structure size. For example, structural elements extending to adjacent properties are a no-no—moreover, structures larger than 35 feet or 10.7 meters across require special installation equipment. Unfortunately, bringing machinery into one’s neighborhood needs a permit.
Another example is a property’s existing layout. The target location must adhere to local building standards. Unfortunately, if local regulations only allow homeowners to build in a specific area, families must make do with available space.
• Greenhouse Purpose
Homeowners who want to propagate seeds and grow seedlings for outdoor transplantation can pick a small-sized greenhouse. Such a structure is affordable, portable, and an excellent choice for beginning backyard farmers and gardeners. A 6-foot by 8-foot (1.82-meter by 2.44-meter) hobby grow house should be sufficient.
On the other hand, families who want to grow different plant varieties (including vegetables) can opt for a larger unit. A 12-foot by 20-foot (3.66-meter by 6.1-meter) building is enough for such a purpose.
However, it is worth noting that homeowners can choose a longer or shorter building, depending on the number and type of crops they wish to grow.
Choosing the location and orientation of the structure is important to optimize its plant growth. According to the University of Georgia, the most productive placement for a hobby greenhouse is in a sunny area to the south or southeast side of a home’s property.
• Plants to Grow
Most plants thrive in the summer showing vigorous growth, while others grow best in the cold months. Installing a single large growhouse to accommodate crops with varying climate requirements is not advisable.
A more appropriate solution is to install a 30- to 35-foot (9.1- to 10.7-meter) greenhouse for each seasonal crop. For example, one unit will grow tomatoes, carrots, eggplants, cucumbers, radishes, and other summer crops.
Another structure will accommodate parsnips, cabbages, Brussels sprouts, leeks, broccolis, kales, and other plants that thrive best in cold months. Of course, in order to grow in these conditions, its necessary to also consider ventilation, electricity with proper light, and heating in adverse weather areas.
Although these factors can influence a family’s greenhouse sizing decisions, the verdict will still depend on available space and budget. Hence, homeowners who want the correct structure size must determine the location and take accurate site measurements. Families with greenhouses have a much better growing, gardening, or backyard farming experience with a large structure.
Visit our backyard greenhouse ideas for more related content.






